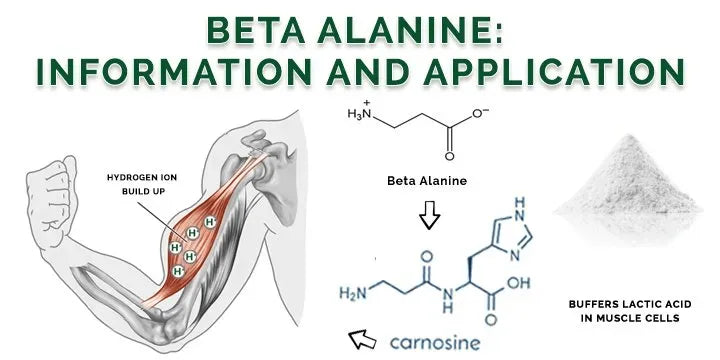
Beta-alanine is a non-essential amino acid that is commonly used as a dietary supplement, particularly among athletes and individuals engaged in high-intensity exercise. Unlike most amino acids, which are used by the body to synthesize proteins, beta-alanine plays a specific role in enhancing athletic performance and endurance.
How Beta-Alanine Works:
- Carnosine Production: Beta-alanine is a precursor to carnosine, a dipeptide (a compound made up of two amino acids) that is stored in high concentrations in skeletal muscles. When you consume beta-alanine, it combines with another amino acid called histidine to form carnosine.
- Buffering Effect: Carnosine acts as a buffer, helping to neutralize the accumulation of hydrogen ions in muscles during intense exercise. This buildup of hydrogen ions is what leads to a decrease in pH, resulting in muscle acidosis, which is associated with fatigue. By buffering these ions, carnosine helps delay the onset of muscle fatigue, allowing for longer and more intense workouts.
Benefits of Beta-Alanine:
-
Improved Athletic Performance: Beta-alanine supplementation is particularly effective in exercises that last between 1 and 4 minutes, such as sprinting, rowing, or high-intensity interval training (HIIT). By delaying fatigue, beta-alanine can help improve performance in these activities.
-
Increased Muscle Endurance: By buffering acid in the muscles, beta-alanine can increase muscle endurance, allowing athletes to perform more repetitions or sustain high-intensity efforts for longer periods.
-
Enhanced Strength Training: For those engaged in strength training, beta-alanine may allow for more repetitions per set, contributing to greater overall strength gains over time.
-
Potential Cognitive Benefits: Some research suggests that carnosine may have neuroprotective properties, possibly benefiting cognitive function, though more studies are needed to confirm these effects.
Dosage and Side Effects:
-
Recommended Dosage: The standard dosage of beta-alanine is typically 2 to 5 grams per day. It's often taken in smaller doses throughout the day to minimize potential side effects.
-
Side Effects: One common side effect of beta-alanine supplementation is a tingling sensation on the skin, known as paresthesia. This is harmless and usually subsides after a short period. To minimize this, beta-alanine can be taken in smaller doses spread throughout the day.
Conclusion:
Beta-alanine is a well-researched supplement that can enhance athletic performance, particularly in high-intensity and endurance activities. By increasing carnosine levels in the muscles, it helps buffer acid buildup, delaying fatigue, and allowing for longer, more intense exercise sessions. While it is generally safe, individuals considering beta-alanine supplementation should be mindful of the dosage to avoid the tingling side effect.